Recommendations on Iron Intake or Iron Supplementation for Women
- Post by: Editor
- August 24, 2021
- Comments off
Iron is a vital mineral necessary to sustain life as formation of red blood cells and transportation of oxygen both dependent on the availability of iron. Lack in daily iron supplementation or intake can cause the anemia leading to death. As per WHO, it has been reported that daily iron supplementation can reduce the risk of anemia and hormonal side effects in menstruating women and adolescent girls.
Fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale or yellowish skin, dizziness and headaches are general symptoms of iron deficiency from low to severe in order. Several reasons could be the cause of iron deficiency including heavy periods in women or giving birth to a baby or malnutrition etc.
Heavy periods can cause rapid iron deficiency and can result in the disruption of whole body mineral balance. If you have following symptoms, it means you are a victim of heavy periods and you should focus on the intake of iron for 3-6 months on weekly basis;
- Needing to change pads or tampons every hour for hours in a row
- Having to double up on pads to absorb your menstrual flow
- Having to change pads or tampons during the night
- Menstrual bleeding that lasts 7 days or longer
- Passing clumps or clots of blood that are larger than a quarter
- Feeling weak or tired when you have your period
- Not being able to do the things you would normally do
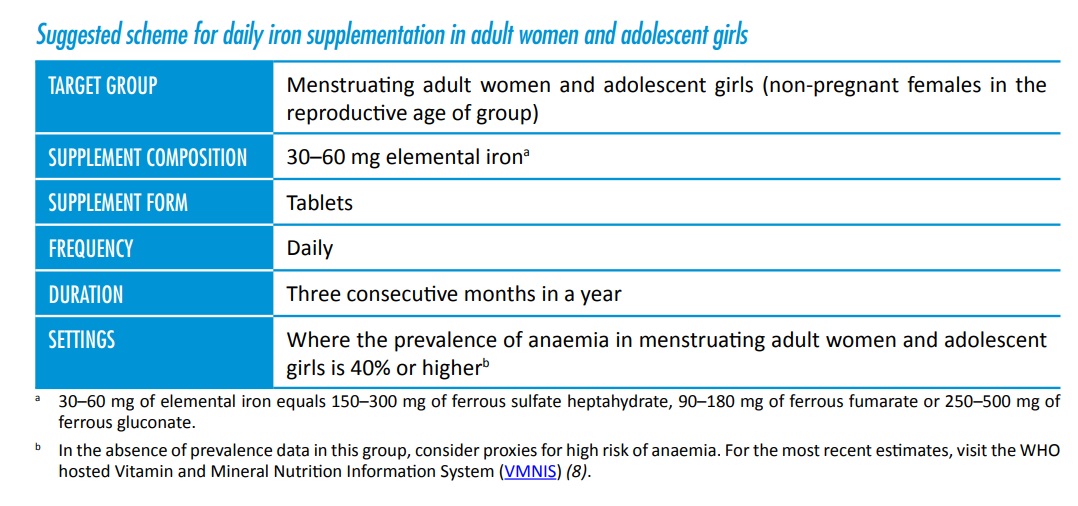
Recommended Dose of Iron intake or Iron Supplementation
Studies have recommended once or twice a week intake of iron for about three to six months, containing 30-60 mg of elemental iron per weekly dose. Composition of elemental iron in available tablets are given in table below (provided by WHO – http://www.who.int/vmnis/en).
Side Effects Associated with Iron intake or Iron Supplementation
Intake of weekly iron for 16 weeks showed higher improvement to hemoglobin concentration while comparing with the continuous daily intake of iron during menstruation for four menstrual cycles. Several studies have explained that to avoid the side effects associated with the intermittent supplementation, recommended daily supplementation of iron should be taken.
Some scientists believe that women should have taken the iron supplementation on weekly basis for longer term rather than daily intake for short period to have fewer or no side effects. Following side effects could be associated with the over dosing of Iron supplementation and if you find any of these symptoms after three months of intake, you should consult with doctor immediately;
More common
- Backache , groin, side, or muscle pain
- chest pain
- chills
- dizziness
- fainting
- fast heartbeat
- fever with increased sweating
- flushing
- headache
- metallic taste
- nausea or vomiting
- numbness, pain, or tingling of hands or feet
- pain or redness at injection site
- redness of skin
- skin rash or hives
- swelling of mouth or throat
- troubled breathing
More common
- Abdominal or stomach pain
- cramping (continuing) or soreness
Less common or rare
- Double vision
- general unwell feeling
- weakness without feeling dizzy or faint
Less common or rare
- Chest or throat pain, especially when swallowing
- stools with signs of blood (red or black color)
Early symptoms of iron overdose
- Diarrhea (may contain blood)
- fever
- nausea
- stomach pain or cramping (sharp)
- vomiting, severe (may contain blood)
Late symptoms of iron overdose
- Bluish-colored lips, fingernails, and palms of hands
- convulsions (seizures)
- pale, clammy skin
- shallow and rapid breathing
- unusual tiredness or weakness
- weak and fast heartbeat
References:
- https://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/micronutrients/guidelines/summary_daily_iron_supp_womenandgirls.pdf?ua=1
- https://www.healthline.com/health/anemia-period#about-anemia
- https://www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/guideline_index/Iron_deficiency/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11890637/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/iron-supplement-oral-route-parenteral-route/side-effects/drg-20070148
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/supplement-guide-iron#1
Note: Please consult with your family physician urgently in case of sever condition and for proper advice as this article is just to provide general awareness about Iron intake based on the authentic sources.